Advantages of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software – Pros & Cons
May 23, 2024 2024-06-17 8:59Advantages of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software – Pros & Cons
Advantages of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software – Pros & Cons
In the realm of design and engineering, innovation is the currency that drives progress. Over the decades, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software has emerged as a cornerstone technology, revolutionizing the way products are conceptualized, developed, and manufactured. This powerful toolset not only enhances efficiency but also empowers designers to realize their creative visions with unparalleled precision. In this article, we’ll explore the advantages of Computer-Aided Design Software and will delve into its applications across various industries, and weigh its benefits and disadvantages.
Table of Contents
Advantages of Computer-Aided Design Software:
The key advantages of Computer-Aided Design software are: Enhanced precision and accuracy, Time efficiency, Cost savings, Versatility & Flexibility and Integration with Manufacturing Processes. Below we have explained the list of benefits of computer aided design software.
1. Enhanced Precision and Accuracy
CAD software enables designers to create intricate designs with utmost precision, down to fractions of a millimeter. This level of accuracy ensures that the final product meets exact specifications, reducing errors and rework during the manufacturing process.
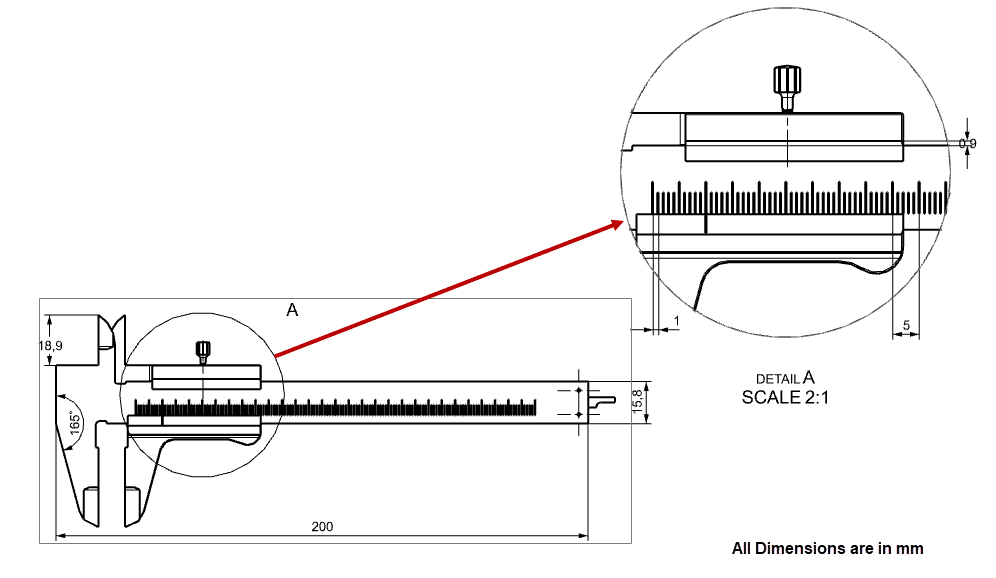
Figure Shows Detailed View of Vernier Caliper with utmost precision
2. Time Efficiency
Traditional design methods involve laborious manual drafting processes, consuming significant time and effort. CAD streamlines this process, allowing designers to create, modify, and analyze designs swiftly. Moreover, CAD facilitates real-time collaboration, enabling multiple stakeholders to work concurrently on a project, thereby reducing time-to-market.3Cost Savings
While initial investment in CAD software and training may seem substantial, the long-term cost savings are undeniable. CAD eliminates the need for physical prototypes, minimizing material wastage and associated expenses. Additionally, CAD allows for virtual testing and simulation, reducing the likelihood of costly design flaws and iterations during the production phase.
3. Versatility and Flexibility
CAD software empowers designers to explore countless design iterations effortlessly. With parametric modeling capabilities, designers can make iterative changes to designs without starting from scratch, fostering creativity and innovation. This flexibility enables rapid prototyping and facilitates the exploration of alternative design concepts.
4. Integration with Manufacturing Processes
CAD software seamlessly integrates with Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems, bridging the gap between design and production. Designs created in CAD can be directly translated into machine-readable formats, facilitating automated manufacturing processes such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting. This integration enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and accelerates time-to-market.
5. Reducing Errors with CAD Models
An effective method for minimizing errors is through the CAD system. For instance, when adjusting the size of a pin, it’s common to overlook resizing the corresponding hole after taking a break. With CAD, designers can ensure that the pin fits into the hole properly by utilizing this feature.
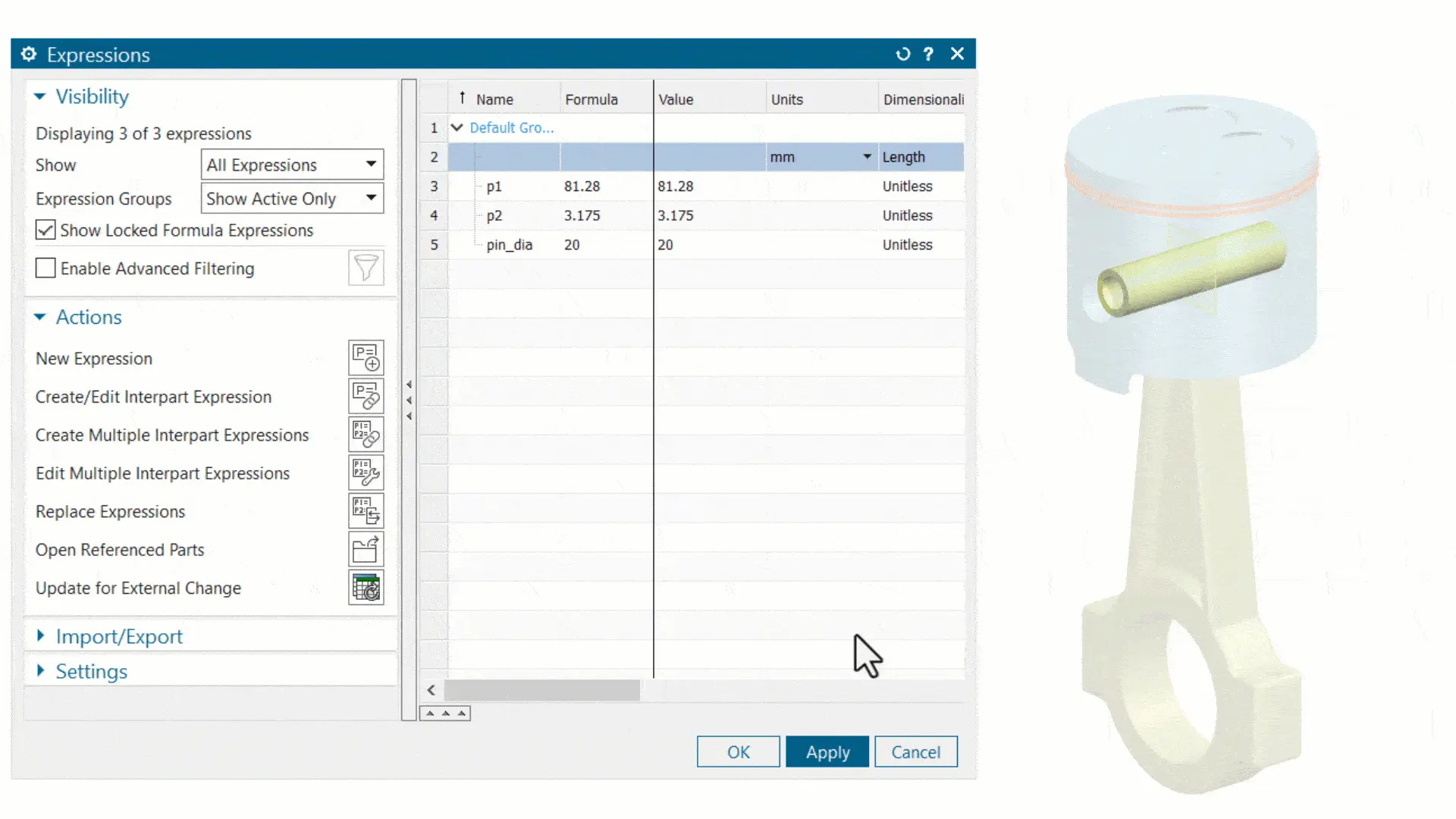
Moreover, depending on the CAD software, these adjustments may occur automatically. If the pin size is modified, the hole dimensions can change accordingly, and these correct dimensions may even be reflected in the 2D drawings.
Disadvantages of Computer-Aided Design Software:
Certainly, while Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software brings a multitude of benefits, it’s important to recognize its limitations and potential disadvantages:
1. High Initial Costs
Purchasing CAD software and the required high-performance hardware can be expensive, posing a significant investment for small businesses or individual users.
2. Steep Learning Curve
CAD software often has complex interfaces and functionalities, necessitating extensive training and practice to achieve proficiency, which can be time-consuming and costly.
3. Dependence on Technology
Reliance on powerful computers and software stability means that technical failures or crashes can disrupt the design process, leading to potential delays and data loss.
4. Data Security Concerns
CAD files contain sensitive information that can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks or unauthorized access, requiring robust security measures to protect intellectual property.
5. Compatibility Issues
Different CAD programs may use incompatible file formats, making it challenging to share and collaborate on designs across different platforms and software versions.
By acknowledging these disadvantages of Computer-Aided Design software and proactively addressing them, designers and organizations can maximize the benefits of CAD software while mitigating potential challenges. Effective training, robust cybersecurity measures, interoperability standards and a balanced approach to design optimization are essential for leveraging CAD technology effectively in today’s competitive landscape.
Uses of Various CAD Softwares With their Benefits
Explore the use of various computer aided design software with their benefits:
1. AutoCAD
Widely used in architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries for 2D drafting and 3D modeling.
Benefits of AutoCAD:
- Versatility in Design: AutoCAD is renowned for its versatility, allowing users to create both 2D drafts and 3D models with high precision.
- Efficiency: Features like automated drafting tools and libraries of pre-designed components speed up the design process.
- Accuracy: Offers tools for exact measurements and detailing, reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Collaboration: Supports DWG file format, which is widely used and easily shared among professionals, enhancing collaborative efforts.
2. SOLIDWORKS
Popular among mechanical engineers for parametric modeling, simulation, and finite element analysis (FEA)
Benefits of SOLIDWORKS:
- Parametric Modeling: Enables users to create models based on parameters, allowing easy adjustments and updates.
- Simulation and Analysis: Integrated simulation tools help in testing and validating designs before manufacturing, ensuring functionality and performance.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): SolidWorks offers solutions for managing the entire lifecycle of a product from inception to disposal, improving overall efficiency.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive interface makes it accessible for both beginners and advanced users.
3. CATIA
Preferred by aerospace and automotive manufacturers for its advanced surface modeling and Advance assembly capabilities.
Benefits of CATIA:
- Complex Surface Modeling: Excels in creating complex and precise surface geometries, essential for high-performance industries.
- Collaborative Design: Allows multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously, improving team productivity.
- Advanced Simulation: Provides comprehensive simulation capabilities, including finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD).
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with other systems and software, enhancing workflow and data management.
4. Siemens NX
Renowned for its advanced capabilities in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery. It excels in 3D model Design, complex surface modeling, simulation and digital twin integration.
Benefits of Siemens NX:
- Integrated Solutions: Siemens NX offers a comprehensive suite of tools that cover the entire product development process, from conceptual design to manufacturing.
- Advanced Simulation: Includes high-level simulation tools for structural, thermal, and fluid dynamics analysis, ensuring product reliability and performance.
- Synchronous Technology: Combines the best of both parametric and direct modeling techniques, providing flexibility in making design changes.
- Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration across different disciplines with integrated data management, improving project coordination and reducing errors.
5. Creo
Employed in diverse industries for product development, from consumer goods to medical devices.
Benefits of Creo:
- Parametric and Direct Modeling: Creo offers both parametric and direct modeling capabilities, allowing designers to choose the best approach for their specific needs.
- Robust Simulation Tools: Integrated simulation features help validate designs under real-world conditions, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
- Scalability: Scales from small projects to large, complex assemblies, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- IoT Integration: Creo supports Internet of Things (IoT) integration, enabling smart product design and connectivity.
6. Autodesk Inventor
Ideal for mechanical engineers and product designers seeking robust 3D design and simulation capabilities.
Benefits Autodesk Inventor:
- Comprehensive 3D Modeling: Autodesk Inventor provides powerful 3D modeling tools that enhance design precision and flexibility.
- Integrated CAD/CAM: Combines CAD and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) functionalities, streamlining the workflow from design to production.
- Simulation and Analysis: Includes simulation capabilities for stress analysis, dynamic simulation, and finite element analysis (FEA), ensuring robust product designs.
- Collaboration Tools: Offers cloud-based collaboration features, allowing teams to work together in real-time, regardless of location.
7. Revit
Dominant in the building information modeling (BIM) space, particularly for architectural design and construction planning.
Benefits of Revit:
- BIM Capabilities: Revit’s BIM features allow for the creation of accurate, data-rich 3D models that support all phases of the building lifecycle.
- Coordination: Improves coordination among different stakeholders (architects, engineers, contractors) by providing a single, updated model.
- Cost Estimation: Helps in cost estimation and material takeoff, leading to better budget management.
- Sustainability: Includes tools for energy analysis and sustainability assessments, promoting green building practices.
8. Fusion 360
Versatile CAD/CAM tool used in product design, industrial machinery, and prototyping.
Benefits of Fusion 360:
- Cloud-Based Platform: Fusion 360’s cloud-based nature allows for easy access and collaboration from anywhere.
- Integrated CAM: Combines CAD and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) in one platform, streamlining the process from design to production.
- Simulation Tools: Offers robust simulation capabilities to test product performance under various conditions.
- Version Control: Tracks changes and manages different versions of a design, facilitating better project management.
9. Rhino
Favored by industrial designers and jewelry makers for its intuitive surface modeling and rendering features.
Benefits of Rhino:
- Precision Modeling: Rhino excels in creating precise and complex geometries, essential for detailed design work.
- Customizability: Supports scripting and plugin development, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs.
- Compatibility: Can import and export a wide range of file formats, facilitating integration with other software.
- Advanced Rendering: Provides advanced rendering options to create photorealistic images of designs.
In conclusion, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software stands as a cornerstone technology in the modern era of design and engineering. Its myriad advantages, from enhanced precision and efficiency to streamlined collaboration and innovation, have reshaped industries and propelled innovation to new heights. While CAD software is not without its challenges, the benefits it offers far outweigh the drawbacks, making it an indispensable tool for designers and engineers alike. As technology continues to evolve, so will the capabilities of CAD software, driving further advancements and unlocking new possibilities in the world of design.
How i GET IT by Tata Technologies can help in Mastering CAD softwares?
i GET IT by Tata Technologies is a premier eLearning solution tailored to enhance the proficiency of mechanical anddesign engineers in utilizing today’s leading MCAD (Mechanical Computer Aided Design) applications and honing their design skills.
Explore our extensive library of courses covering AutoDesk, AutoCAD, SOLIDWORKS, Catia V5, and a host of other cutting-edge design solutions. With i GET IT, you can access in-depth e-learning modules, tech tips, and new courses designed to sharpen your skills and stay ahead in the ever-evolving field of engineering design.
Embark on your upskilling journey today by visiting https://www.myigetit.com and take the next step towards mastering CAD software and advancing your career.
For any inquiries or assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us at igetitsupport@tatatechnologies.com.
Unlock your potential with i GET IT. Start learning, start achieving.
Megharaj
Related Posts
Series & Parallel Hybrid Vehicles: Are they Outsmarting EVs?
What is Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM)? [Detailed Guide]
Top 5 Mechanical Design Engineer Courses by Tata Technologies
What is Single Line Diagram? – Meaning, Importance & Example
Is Mechanical Engineering a Good Career for the Future?
Find
Categories
Latest Posts
Popular Tags



















