Independent Front Wheel Suspension – Types, Benefits & Working
November 10, 2025 2025-12-02 11:53Independent Front Wheel Suspension – Types, Benefits & Working
Independent Front Wheel Suspension – Types, Benefits & Working
In the early days of automobiles, most vehicles relied on solid axle suspensions because of their simplicity, strength, and ability to carry heavy loads. This design linked both wheels on the same axle, making it durable and easy to manufacture, which suited the rough roads of the time. However, as vehicles became faster and passenger comfort grew more important, the drawbacks of solid axles became clear. To overcome these limitations, engineers introduced independent wheel suspension systems, allowing each wheel to move separately. This innovation in independent wheel suspension dramatically improved ride quality, stability, and cornering performance. Over time, independent wheel suspension—particularly at the front—became the standard in passenger cars, as it offered the perfect balance between comfort, control, and safety.
Table of Contents
Evolution of Suspension Systems
In today’s automotive landscape, suspension systems are fundamental to achieving stability, comfort, and precise control. Among the different suspension designs, the Independent Wheel Suspension has become a widely used solution because it allows each wheel to respond to road conditions individually, minimizing the transfer of shocks and vibrations across the vehicle. This design not only improves passenger comfort but also enhances vehicle handling and safety under dynamic driving conditions.
As the field of automotive engineering continues to evolve, the importance of advanced suspension technologies has only increased. Independent Wheel Suspension, in particular, stands out for delivering superior ride quality and manoeuvrability compared to conventional solid axle arrangements. In this article, we will explore the concept in detail, focusing on Independent Front Suspension (IFS)—its working principles, variations, advantages, and how it compares with traditional designs.
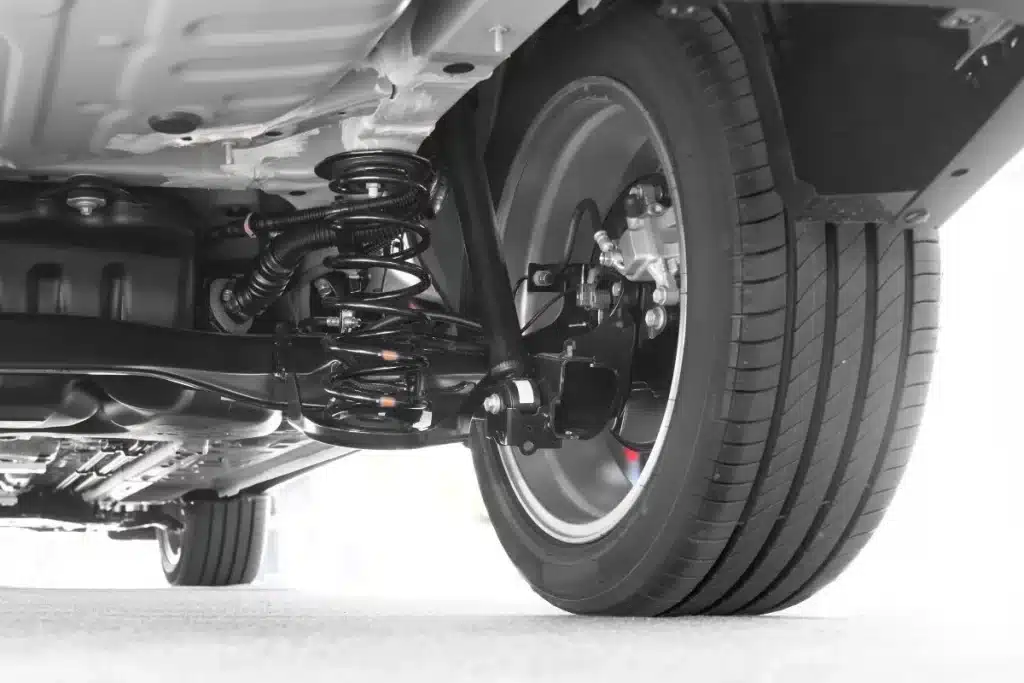

Types of Suspension Systems
Suspension systems are generally classified into two main categories based on how the wheels are connected and how they respond to road irregularities. These are Dependent Suspension and Independent Suspension.
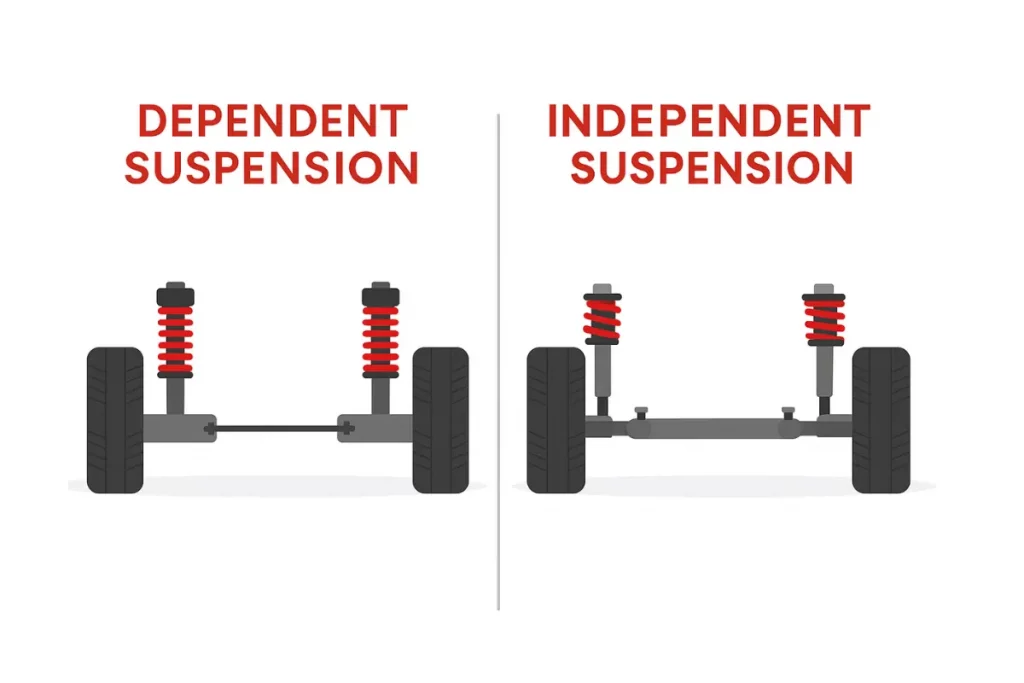
Dependent Suspension (Linked Wheel Suspension)
In this setup, both wheels on the same axle are mechanically connected.
When one wheel moves upward or downward due to a road irregularity, the opposite wheel is also influenced because of the rigid axle connection.
While this design compromises ride comfort, it offers greater durability, load-carrying capacity, and strength, which is why it’s often used in heavy-duty vehicles.
Essence: Wheel movement is interlinked.
Independent Suspension (Isolated Wheel Suspension)
In this design, each wheel is mounted separately, allowing it to move without disturbing the other wheel on the axle.
A bump affecting one wheel does not transfer the motion to the other, resulting in smoother rides, better handling, and improved stability, especially at higher speeds.
This system is widely used in modern passenger vehicles, where the main focus is on comfort and handling.
Essence: Wheel movement is independent and isolated.
What is Independent Front Suspension?
Independent Front Suspension (IFS) refers to a suspension setup in which each front wheel is able to move up and down without affecting the motion of the other wheel. In contrast to solid axle systems, in which both wheels are fixed together and action on one side influences the other, IFS makes sure that road bumpiness experienced by one wheel does not affect the other wheel. This configuration increases ride comfort, steering accuracy, and vehicle stability overall.
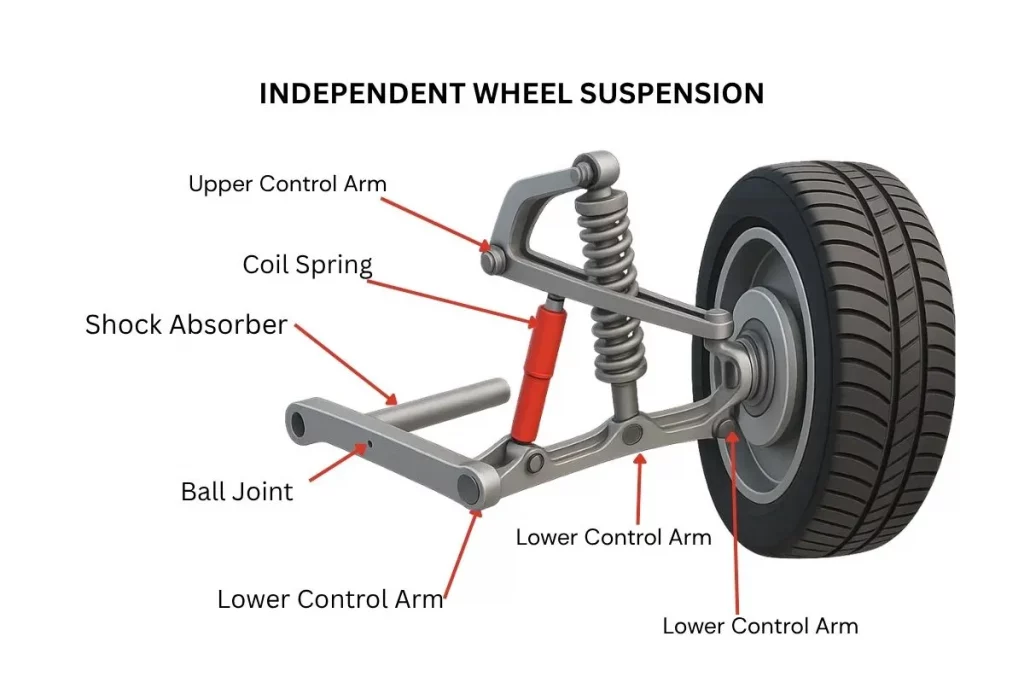
How Independent Front Suspension Works
The core principle of Independent Front Suspension lies in allowing each wheel to move independently without influencing the other. Each wheel is attached to the vehicle chassis by its own suspension components and can respond as an individual unit to roadways. Major pieces are:
Control Arms: These components link the wheel hub to the vehicle’s frame and guide the wheel’s up-and-down motion.
Springs: Usually coil springs, which take up bumps from road inconsistencies.
Shock Absorbers (Dampers): These absorb the energy of the springs, managing oscillations.
Ball Joints and Bushings: They enable smooth motion and help reduce friction between connected components. This design makes it such that when a single wheel goes over a bump or dip, its motion doesn’t affect the other wheel directly, resulting in improved tire contact with the road and improved handling.
Types of Independent Front Suspension Systems
A number of IFS designs have emerged over the years, each having its own characteristics:
1. MacPherson Strut Suspension:
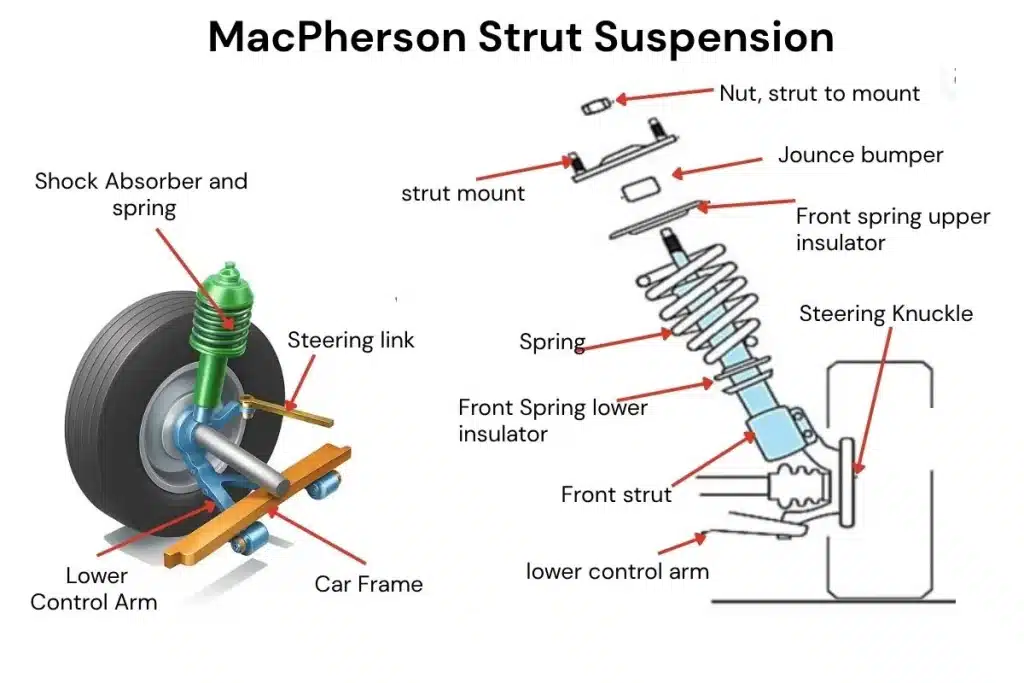
- Houses a shock absorber and coil spring in one unit.
- Simplifies the suspension system, saving weight and money.
- Often employed in front-wheel-drive cars
2.Double Wishbone Suspension:
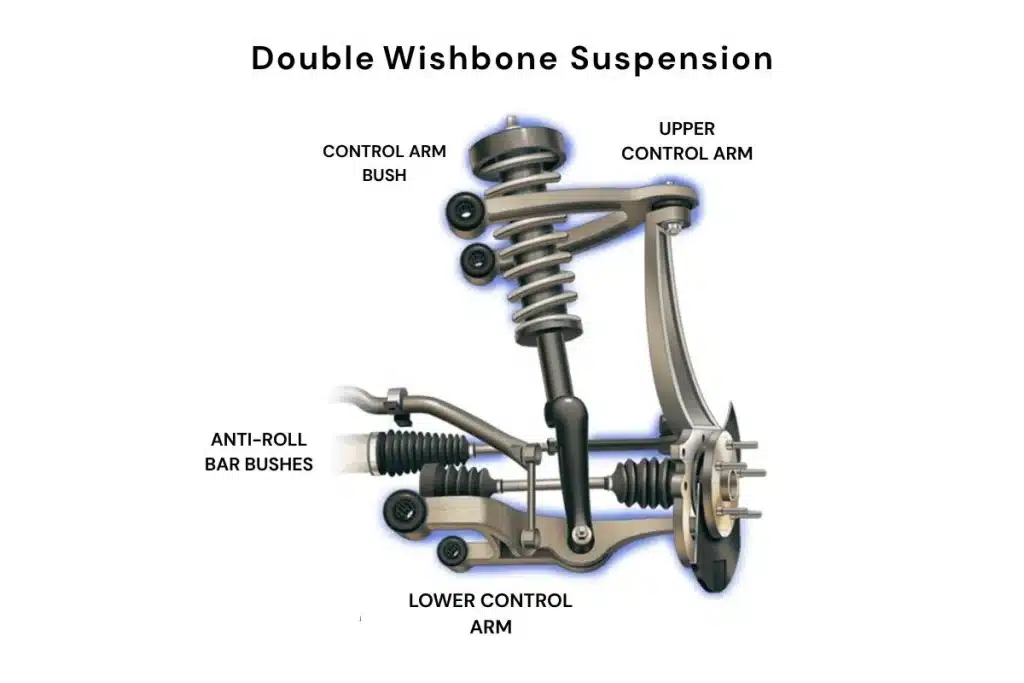
- It utilizes an upper and a lower control arm to manage the movement of the wheel.
- Provides excellent control of wheel alignment and handling.
- Preferred in performance and luxury cars.
3.Multi-Link Suspension:
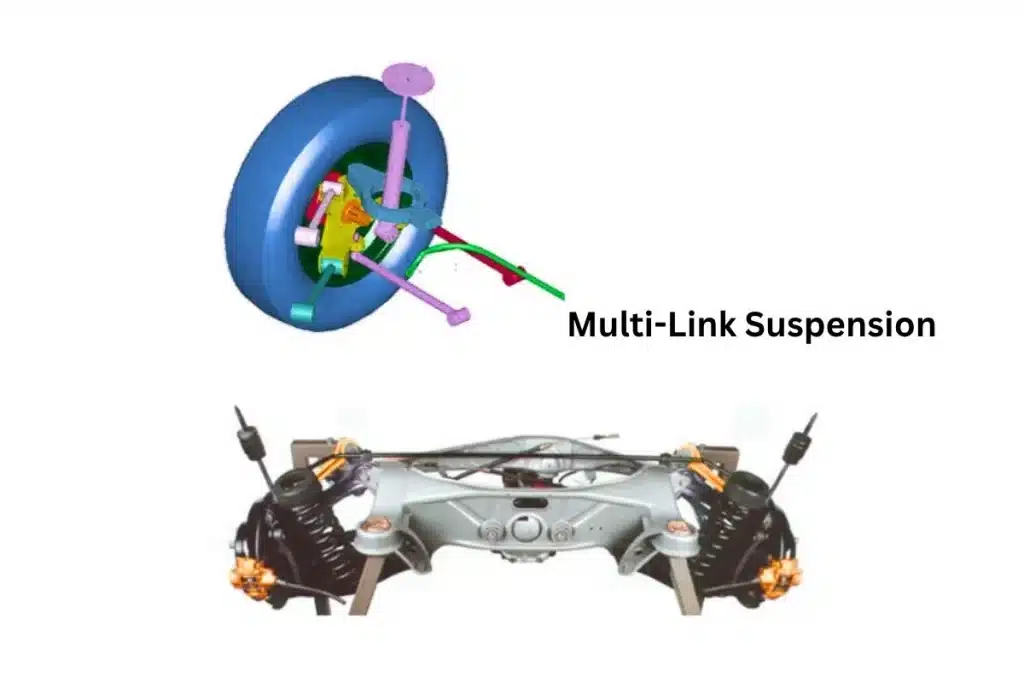

- Employs multiple arms to control wheel movement.
- Offers flexibility in adjustment of ride and handling traits.
- Typically used in high-end and sports vehicles.
4. Torsion Bar Suspension:
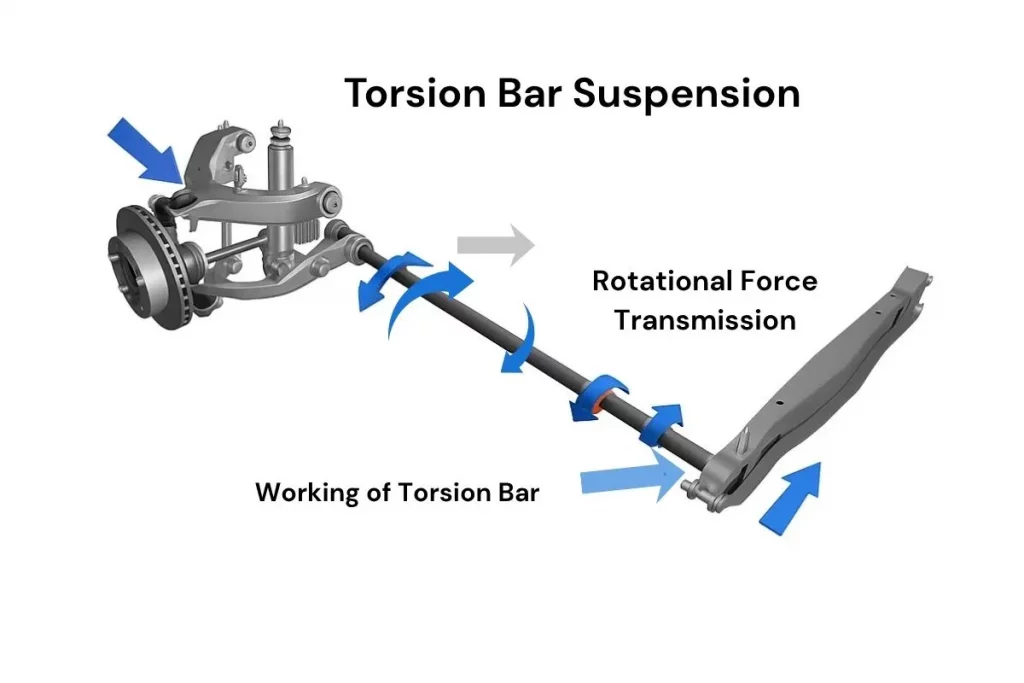
- It relies on a steel bar that twists to provide the spring effect.
- Facilitates simple ride height adjustments.
- Found in most trucks and SUVs.
5. Leaf Spring Suspension:
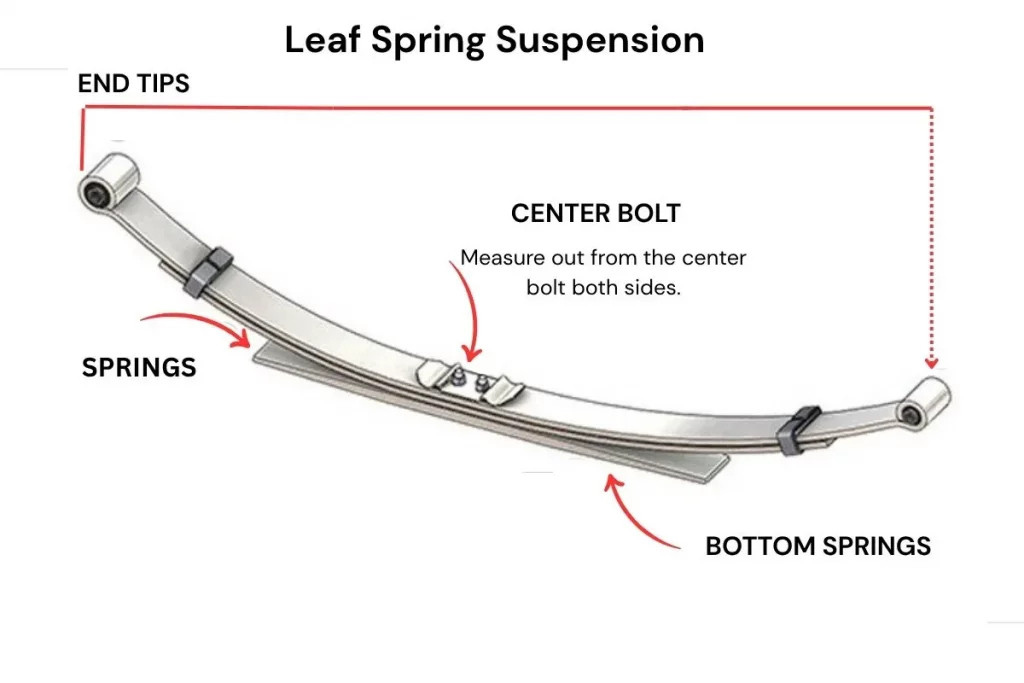
- Comprises stacked metal strips that flex under load.
- DurabN le and simple design.
- Less commonly used in contemporary front suspensions but still applied in some models.
Each of these systems provides a compromise among ride comfort, handling, and manufacturing factors so that manufacturers can select based on the desired vehicle performance and cost objectives.
Advantages of Independent Front Suspension
Use of an IFS system offers the following advantages:
- Improved Ride Comfort: As each wheel can respond independently, the system has a better capability to absorb road irregularities, resulting in improved ride comfort.
- Better Handling: Independent movement means better tire contact with the ground, improving the steering response and stability of the vehicle.
- Less Unsprung Weight: Items such as the differential are attached to the chassis instead of the axle, lowering the weight that moves along with the wheels and enhancing suspension responsiveness.
- Improved Traction: Stable tire contact enhances grip, particularly while cornering and on rough ground.
Disadvantages of Independent Front Suspension
Although the IFS system brings many advantages, it also has some limitations:
Higher Manufacturing Cost: Due to its sophisticated structure and the number of parts involved, producing and repairing IFS is generally more expensive than solid axle designs.
Reduced Toughness in Extreme Use: When exposed to heavy payloads or rough off-road driving, IFS components may not withstand stress as effectively as a solid axle.
Frequent Servicing Needs: Parts such as bushings, ball joints, and control arms experience wear over time and demand routine inspection or replacement.
Complex Repair Work: The advanced arrangement of components can make diagnosing issues and carrying out repairs more complicated and time-intensive.
Independent Front Suspension vs. Solid Axle
On comparing IFS with solid axle systems, the following differences become apparent:
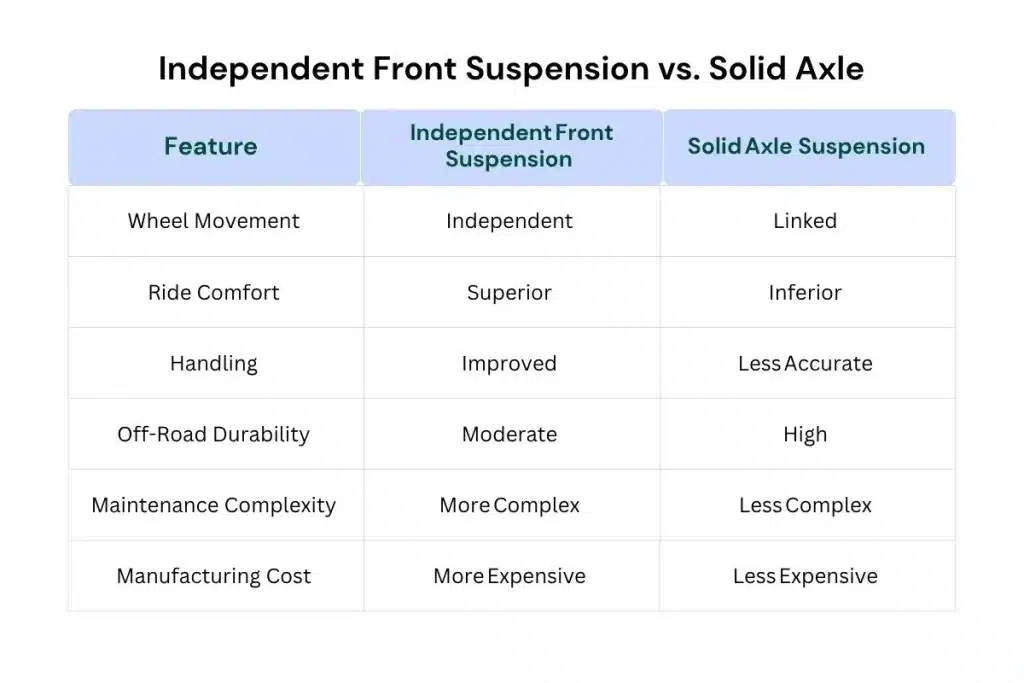
Mastering systems like Independent Front Suspension starts with the right foundation in CAD and design tools. Learn more in our detailed article — Top Automotive Design Engineer Courses by Tata Technologies
Applications of Independent Suspension
Independent suspension systems are widely used in vehicles where comfort, stability, and handling are top priorities. Some common applications include:
Passenger Cars: Most modern cars use independent suspension at the front—and often at the rear—to provide smoother rides and better control.
Luxury and Premium Vehicles: High-end cars rely on advanced independent suspension setups to deliver superior comfort and precise handling.
Sports and Performance Cars: Independent suspension helps maintain tire contact during high-speed cornering, improving grip and responsiveness.
Light Trucks and SUVs: Many adopt independent front suspension to balance off-road capability with on-road comfort.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): With a focus on ride refinement and advanced chassis design, EVs often feature independent suspension systems.
FAQs on Independent Front Wheel Suspension
Independent front suspension is used to enhance ride comfort, road grip, and handling. Since each wheel reacts separately to road conditions, it minimizes vibrations, keeps the car stable during turns, and ensures a smoother drive for passengers.
The key components include upper and lower control arms, coil springs, shock absorbers, ball joints, and an anti-roll bar. These parts work together to support the vehicle’s weight, absorb road irregularities, and maintain tire contact for consistent traction.
Independent suspension improves handling by allowing each wheel to maintain maximum road contact. This reduces body roll during cornering, enhances steering precision, and ensures better control, especially at high speeds or on uneven terrain.
The suspension system experiences vertical loads (vehicle weight), lateral forces (cornering), and longitudinal forces (acceleration/braking). Proper suspension geometry distributes these forces evenly, ensuring stability, reducing tire wear, and improving ride comfort.
Most modern cars come with independent front suspension because it offers superior comfort and control. However, heavy-duty trucks and off-road vehicles often use dependent (solid axle) suspension systems for better strength, durability, and load-bearing capacity.
Yes, electric vehicles (EVs) commonly use independent suspension systems. This design enhances comfort, supports precise handling, and provides space-efficient packaging for battery placement, maintaining a low center of gravity for improved balance and energy efficiency.
The function of Independent Front Suspension is to let each front wheel move independently over road irregularities. This improves ride comfort, steering control, and vehicle stability by maintaining better tire contact with the road.
Independent Front Suspension is used in most modern passenger cars, SUVs, and light trucks. It is also common in luxury, performance, and electric vehicles for improved comfort and precise handling.
Independent suspension is better than a rigid axle because it provides a smoother ride, better traction, and enhanced handling. Each wheel moves separately, so bumps on one side don’t affect the other, ensuring greater stability and comfort.
Yes. Suspension systems can be modeled and analyzed using CAD software like SOLIDWORKS, CATIA, or Autodesk Fusion 360. These tools help engineers create 3D models, perform motion analysis, and test suspension performance under real-world conditions.
Manjunath
Related Posts
What is Fluid Mechanics? – Introduction, Laws & Equations
What Is AutoCAD Software? Uses, Features & Practical Examples
What is PLM? – Product Lifecycle Management [Detailed Guide]
Lead-Acid vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries: Key Differences & Best Uses
Top AutoCAD 3D Commands & Shortcuts with Examples
Find
Categories
Latest Posts
What is Fluid Mechanics? – Introduction, Laws & Equations
January 7, 2026What Is AutoCAD Software? Uses, Features & Practical Examples
December 18, 2025Independent Front Wheel Suspension – Types, Benefits & Working
November 10, 2025Popular Tags



















